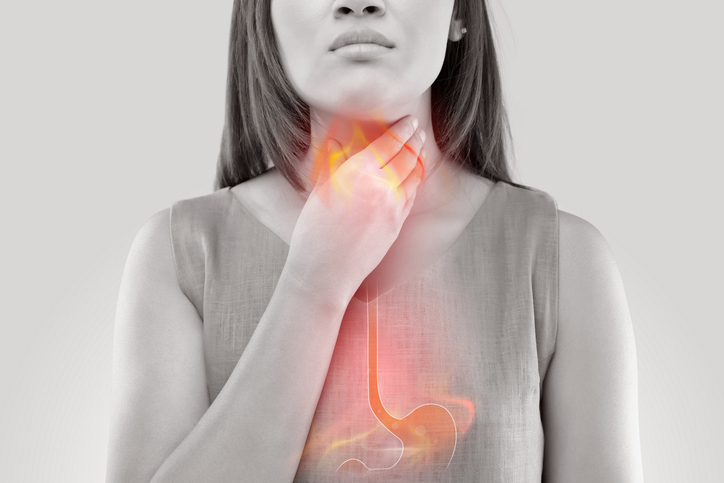
Swallowing disorders encompass trouble with swallowing and is referring to two different problems: Dysphagia — which is the sensation of fluid or food being regurgitated or stuck in the chest; also any throat issue leading to choking or coughing while you’re swallowing. Swallowing disorders can cause problems in everyday life, although they are treatable by a doctor. Dr. Madison Richardson is skilled and experienced and offers treatment for swallowing disorders, and dysphagia treatment. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, or have already been diagnosed with dysphagia, you should contact a doctor for treatment and help. Schedule your appointment with Dr. Madison Richardson in his Beverly Hills doctor’s office as soon as possible.

Symptoms of Dysphagia
There are certain signs of dysphagia to look out for, including:
- Pain when you swallow
- Being unable to swallow
- Feeling as if food is stuck in your chest, throat, or the back of your breastbone
- Regurgitation
- Drooling
- Stomach acid or food backing into your throat
- Feeling hoarse in the throat
- sudden weight loss
- Reoccurring heartburn
- Gagging or coughing when you swallow
When to see Dr. Richardson
You should make an appointment with Dr. Richardson as soon as possible if you are noticing the symptoms listed above, or if your dysphagia is also causing you to experience vomiting, regurgitation, or weight loss. If you feel as if there is an obstruction in your throat that is hindering your ability to breathe, call 911 immediately.
Causes of dysphagia
Swallowing is an intricate internal process that incorporates many different nerves and muscles. Anything that leads to muscle or nerve damage, or weakening, of the throat can lead to the development of dysphagia.
There are two main categories of dysphagia.
Esophageal dysphagia
This is referring to the feeling of food being lodged or stuck in the back of your throat or chest after you swallow. Some causes of this type of dysphagia include:
- Achalasia. When the bottom esophageal muscle will not relax the way it is supposed to in order to allow the food to enter the stomach, causing it to come back up the throat. The muscles in the esophagus wall might be weak as well, and this usually gets worse over time.
- Diffuse spasm. This is a condition that causes the esophagus to have uncoordinated, high-pressure spasms after swallowing. These spasms happen in the involuntary lower esophagus muscles.
- Esophageal stricture. This is when large pieces of food will get stuck in a narrow esophagus. The narrowing of the esophagus is typically caused by scar tissue or tumors from GERD.
- Esophageal tumors. If you have a tumor in your esophagus, swallowing issues will usually worsen as time goes on due to your esophagus getting more narrow.
- Foreign bodies. It is possible for an object or food to block the esophagus either partially or fully. People with dentures or that have a hard time chewing will be more likely to develop this issue.
- Esophageal ring. A smaller area of the esophagus that has narrowed can cause you to have a hard time swallowing.
- GERD. (Or Gastroesophageal reflux disease) causes damage to the tissue in the esophagus from stomach acid coming into the throat that may lead to scarring or narrowing of the bottom esophagus.
- Eosinophilic esophagitis. This is often in relation to an allergic food reaction and causes the development of too many eosinophils cells in the esophagus.
- Scleroderma. Scar tissue develops which causes the hardening and stiffening of tissues in the bottom esophagus. This causes acid to come back up and the feeling of heartburn.
- Radiation therapy. Certain cancer treatments can cause inflammation and scar tissue development in the esophagus.
Oropharyngeal dysphagia
There are some conditions that can make your throat muscles weaken, which makes moving food through its regular digestion path difficult. You might experience coughing gagging, or choking when attempting to swallow. You might also experience a feeling of food or liquid going down your throat or up your nose, which has the possibility of developing into pneumonia.
A few factors that lead to this type of dysphagia are:
- Radiation therapy. Certain cancer treatments can cause inflammation and scar tissue development in the esophagus.
- Neurological damage. A stroke or injury to the spinal cord or brain can cause you to have a hard time swallowing.

book an appointment